Facts You Should Know About Skin Cancer Examinations
Skin cancer is a prevalent and potentially deadly condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Regular Skin Cancer Screen and Exams are crucial for early detection and treatment. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer globally. It occurs when skin cells are damaged by ultraviolet (UV) radiation, leading to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells.
Types of Skin Cancer:
The three main types of Skin Cancer Screen and Exams are basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma. BCC and SCC are more common and have high cure rates if detected early, while melanoma is more aggressive and can spread rapidly.
Risk Factors:
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds is a significant risk factor for developing skin cancer. Other risk factors include fair skin, a history of sunburns, a weakened immune system, and a family history of skin cancer.
Importance of Early Detection:
Early detection is crucial for successful skin cancer treatment. Regular skin examinations can help identify suspicious moles or lesions before they become more advanced and difficult to treat.
Self-Examinations:
Individuals are encouraged to perform regular self-examinations of their skin. This involves checking moles, freckles, and other skin abnormalities for changes in size, color, shape, or texture. Any suspicious changes should be promptly reported to a healthcare professional.
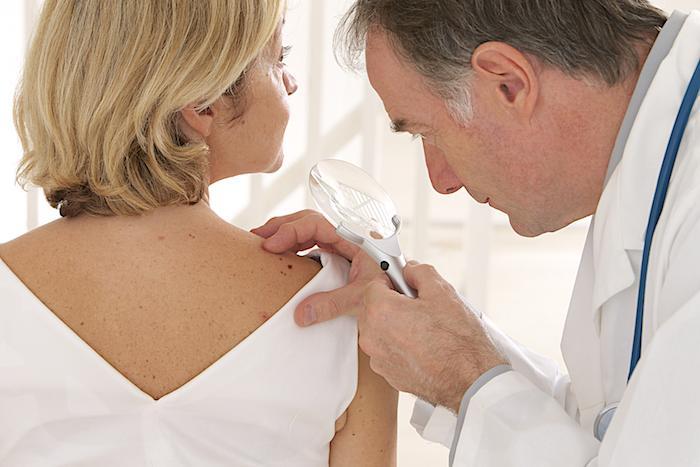
Professional Skin Examinations:
Dermatologists are specialized in skin health and can conduct thorough skin examinations. It is advisable to schedule regular appointments with a dermatologist for professional skin checks, especially for individuals with a higher risk of skin cancer.
Frequency of Examinations:
The frequency of skin examinations depends on individual risk factors. High-risk individuals, such as those with a history of skin cancer or extensive sun exposure, may need more frequent checks.
Mole Mapping:
Mole mapping is a technique used by dermatologists to monitor and track changes in moles over time. This involves photographing and documenting the size, color, and other characteristics of each mole, providing a baseline for future comparisons.
Biopsy for Diagnosis:
If a suspicious lesion is identified during a skin examination, a biopsy may be performed to determine if it is cancerous. This involves removing a small sample of tissue for laboratory analysis.
Sun Protection Measures:
Prevention is key to reducing the risk of skin cancer. Sun protection measures, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure, are essential components of a skin cancer prevention strategy.
Early Treatment Options:
If skin cancer is detected early, treatment options such as surgery, cryotherapy, or topical medications may be effective. Timely intervention can often prevent the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.